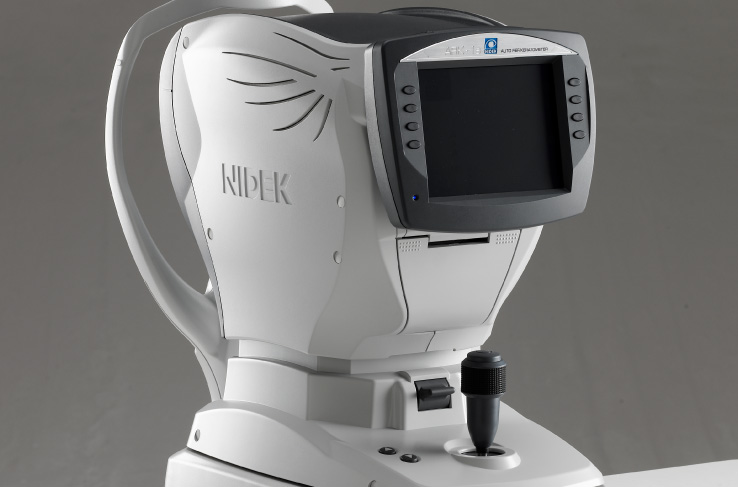
Home/Auto Ref/Keratometer / Auto Refractometer ARK-1s/1a/1 AR-1s/1a/1
Auto Ref/Keratometer / Auto Refractometer
ARK-1s/1a/1 AR-1s/1a/1
Brand : Nidek – Japan
The ARK/AR series speak for themselves, surpassing a conventional auto ref/keratometer and auto refractometer with technologically enhanced functions generating greater accuracy and greater clinical information.
Superior Functions for Superior Outcomes
- Accurate Refraction Measurement
- VA Measurement with Glare Test
- Simple Opacity Assessment
- Patient-friendly Accommodation Measurement
Large Pupil Zone Imaging Method
The large pupil zone imaging method enables the measurement of wide area refraction of up to 6 mm diameter and can indicate the difference between wide area refraction and the central area refraction of up to 3.5 mm diameter. The pupil diameter is measured simultaneously. The difference of the measurement allows assessment of the effect of pupil size such as a vision in dim light.
Super Luminescent Diode and Highly Sensitive CCD
Incorporation of the Super Luminescent Diode (SLD) provides a sharper and clearer image compared to a conventional LED. The highly sensitive CCD detects the ring image even if the fundus reflection is weak. The system combining the SLD and highly sensitive CCD significantly improves measurement capability even in dense cataractous eyes.
Optimal Fogging to Minimize Accommodation (available for the ARK-1s, ARK-1a, AR-1s, and AR-1a)
Fogging is performed after correcting the patient’s astigmatism with built-in cylinder lenses. This allows the patient to view the target clearly and minimizes the interference with accommodation even in high astigmatism.
Accommodation Measurement with Artificial Intelligence Algorithm
Objective measurement of accommodation is performed with patient’s focusing on a target which moves from distance to near. The artificial intelligence algorithm detects the patient’s response and reduces the measurement time in cases with a slow or weak accommodative response. The accommodation measurement helps to assess pseudomyopia, eyestrain, and accommodative palsy.